Ich dachte, dies wäre ein relativ einfaches Problem, aber ich verbrachte ein paar Tage damit, herauszufinden, wie zum Teufel man Pendelbewegungen simuliert. Ich wollte nicht schummeln und nur die x-, y-Position basierend auf den Kurven sin (Theta) und cos (Theta) ändern. Stattdessen wollte ich mich mit den beiden Kräften befassen, die im wirklichen Leben angewendet werden, Schwerkraft und Spannung . Das Hauptstück, das mir fehlte, war die Zentripetalkraft.
Die Wikipedia-Seite Pendel (Mathematik) enthält eine großartige Animation (unten links), die die Pendelbewegung erklärt. Sie können sehen, dass mein Ergebnis (rechts) diesem Diagramm auffallend ähnlich ist
Der "Bob" ist das schwingende Objekt und der "Pivot" ist der Ursprung / die Wurzel.
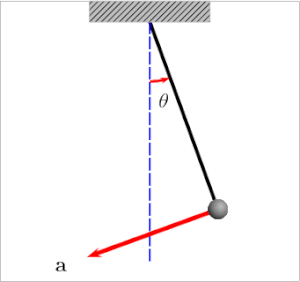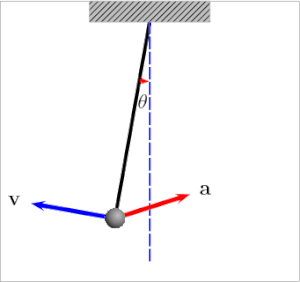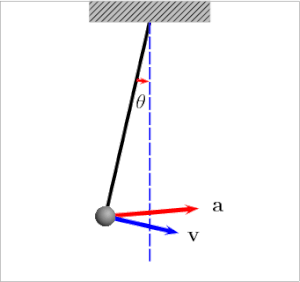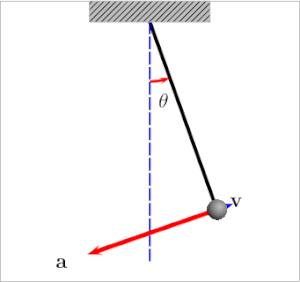

Ich fand auch diesen Artikel und das Diagramm (unten) ziemlich hilfreich:

Theta entspricht dem Winkel zwischen dem Seil und der Richtung der Schwerkraft.
Wenn sich der Bob links oder rechts befindet, ist die Spannung gleich:

Der Grund, warum die Spannungskraft größer ist, wenn sich der Bob dem Gleichgewichtspunkt (Mitte) nähert, liegt in der Zentripetalkraft :

Die Formel für die Gesamtspannung sieht also so aus, wie der Bob schwingt:

Es gibt zwei Kräfte im Pendelsystem:
- Schwere
GravityForce = mass * gravity.magnitudeGravityDirection = gravity.normalized
- Spannung
TensionForce = (mass * gravity * Cos(theta)) + ((mass * velocityTangent^2)/ropeLength)TensionDirection = ropeDirection = bob to pivot
Wenden Sie einfach die Schwerkraft auf Ihr Objekt an, wie Sie es für ein normales Objekt tun würden, und wenden Sie dann die Spannung an. Wenn Sie die Kräfte anwenden, multiplizieren Sie die Kraft einfach mit der Richtung und der DeltaTime.
Unten ist das Pendulum.csSkript (auch als GitHub Gist ). Es funktioniert recht gut, aber es gibt einige Rundungsfehler, wenn Sie es für eine Weile verlassen (kehrt nicht zu genau derselben Position zurück).
Das Skript funktioniert in 3D, aber natürlich schwingt ein Pendel nur in einer 2D-Ebene. Es funktioniert auch mit der Schwerkraft in jede Richtung. Wenn Sie beispielsweise die Schwerkraft umkehren, arbeitet das Pendel verkehrt herum.Edit->Project Settings->Physics->Gravity
Es ist sehr wichtig, beim Aktualisieren des Pendels eine konsistente, relativ kleine DeltaTime zu haben, damit Sie nicht um die Kurve springen. Ich verwende die in diesem Artikel beschriebene Technik, FIX YOUR TIMESTEP! von Glenn Fiedler , um dies zu erreichen. Überprüfen Sie die Update()Funktion unten, um zu sehen, wie ich sie implementiert habe.

using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
// Author: Eric Eastwood (ericeastwood.com)
//
// Description:
// Written for this gd.se question: http://gamedev.stackexchange.com/a/75748/16587
// Simulates/Emulates pendulum motion in code
// Works in any 3D direction and with any force/direciton of gravity
//
// Demonstration: https://i.imgur.com/vOQgFMe.gif
//
// Usage: https://i.imgur.com/BM52dbT.png
public class Pendulum : MonoBehaviour {
public GameObject Pivot;
public GameObject Bob;
public float mass = 1f;
float ropeLength = 2f;
Vector3 bobStartingPosition;
bool bobStartingPositionSet = false;
// You could define these in the `PendulumUpdate()` loop
// But we want them in the class scope so we can draw gizmos `OnDrawGizmos()`
private Vector3 gravityDirection;
private Vector3 tensionDirection;
private Vector3 tangentDirection;
private Vector3 pendulumSideDirection;
private float tensionForce = 0f;
private float gravityForce = 0f;
// Keep track of the current velocity
Vector3 currentVelocity = new Vector3();
// We use these to smooth between values in certain framerate situations in the `Update()` loop
Vector3 currentStatePosition;
Vector3 previousStatePosition;
// Use this for initialization
void Start () {
// Set the starting position for later use in the context menu reset methods
this.bobStartingPosition = this.Bob.transform.position;
this.bobStartingPositionSet = true;
this.PendulumInit();
}
float t = 0f;
float dt = 0.01f;
float currentTime = 0f;
float accumulator = 0f;
void Update()
{
/* */
// Fixed deltaTime rendering at any speed with smoothing
// Technique: http://gafferongames.com/game-physics/fix-your-timestep/
float frameTime = Time.time - currentTime;
this.currentTime = Time.time;
this.accumulator += frameTime;
while (this.accumulator >= this.dt)
{
this.previousStatePosition = this.currentStatePosition;
this.currentStatePosition = this.PendulumUpdate(this.currentStatePosition, this.dt);
//integrate(state, this.t, this.dt);
accumulator -= this.dt;
this.t += this.dt;
}
float alpha = this.accumulator/this.dt;
Vector3 newPosition = this.currentStatePosition*alpha + this.previousStatePosition*(1f-alpha);
this.Bob.transform.position = newPosition; //this.currentStatePosition;
/* */
//this.Bob.transform.position = this.PendulumUpdate(this.Bob.transform.position, Time.deltaTime);
}
// Use this to reset forces and go back to the starting position
[ContextMenu("Reset Pendulum Position")]
void ResetPendulumPosition()
{
if(this.bobStartingPositionSet)
this.MoveBob(this.bobStartingPosition);
else
this.PendulumInit();
}
// Use this to reset any built up forces
[ContextMenu("Reset Pendulum Forces")]
void ResetPendulumForces()
{
this.currentVelocity = Vector3.zero;
// Set the transition state
this.currentStatePosition = this.Bob.transform.position;
}
void PendulumInit()
{
// Get the initial rope length from how far away the bob is now
this.ropeLength = Vector3.Distance(Pivot.transform.position, Bob.transform.position);
this.ResetPendulumForces();
}
void MoveBob(Vector3 resetBobPosition)
{
// Put the bob back in the place we first saw it at in `Start()`
this.Bob.transform.position = resetBobPosition;
// Set the transition state
this.currentStatePosition = resetBobPosition;
}
Vector3 PendulumUpdate(Vector3 currentStatePosition, float deltaTime)
{
// Add gravity free fall
this.gravityForce = this.mass * Physics.gravity.magnitude;
this.gravityDirection = Physics.gravity.normalized;
this.currentVelocity += this.gravityDirection * this.gravityForce * deltaTime;
Vector3 pivot_p = this.Pivot.transform.position;
Vector3 bob_p = this.currentStatePosition;
Vector3 auxiliaryMovementDelta = this.currentVelocity * deltaTime;
float distanceAfterGravity = Vector3.Distance(pivot_p, bob_p + auxiliaryMovementDelta);
// If at the end of the rope
if(distanceAfterGravity > this.ropeLength || Mathf.Approximately(distanceAfterGravity, this.ropeLength))
{
this.tensionDirection = (pivot_p - bob_p).normalized;
this.pendulumSideDirection = (Quaternion.Euler(0f, 90f, 0f) * this.tensionDirection);
this.pendulumSideDirection.Scale(new Vector3(1f, 0f, 1f));
this.pendulumSideDirection.Normalize();
this.tangentDirection = (-1f * Vector3.Cross(this.tensionDirection, this.pendulumSideDirection)).normalized;
float inclinationAngle = Vector3.Angle(bob_p-pivot_p, this.gravityDirection);
this.tensionForce = this.mass * Physics.gravity.magnitude * Mathf.Cos(Mathf.Deg2Rad * inclinationAngle);
float centripetalForce = ((this.mass * Mathf.Pow(this.currentVelocity.magnitude, 2))/this.ropeLength);
this.tensionForce += centripetalForce;
this.currentVelocity += this.tensionDirection * this.tensionForce * deltaTime;
}
// Get the movement delta
Vector3 movementDelta = Vector3.zero;
movementDelta += this.currentVelocity * deltaTime;
//return currentStatePosition + movementDelta;
float distance = Vector3.Distance(pivot_p, currentStatePosition + movementDelta);
return this.GetPointOnLine(pivot_p, currentStatePosition + movementDelta, distance <= this.ropeLength ? distance : this.ropeLength);
}
Vector3 GetPointOnLine(Vector3 start, Vector3 end, float distanceFromStart)
{
return start + (distanceFromStart * Vector3.Normalize(end - start));
}
void OnDrawGizmos()
{
// purple
Gizmos.color = new Color(.5f, 0f, .5f);
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(this.Pivot.transform.position, this.ropeLength);
Gizmos.DrawWireCube(this.bobStartingPosition, new Vector3(.5f, .5f, .5f));
// Blue: Auxilary
Gizmos.color = new Color(.3f, .3f, 1f); // blue
Vector3 auxVel = .3f * this.currentVelocity;
Gizmos.DrawRay(this.Bob.transform.position, auxVel);
Gizmos.DrawSphere(this.Bob.transform.position + auxVel, .2f);
// Yellow: Gravity
Gizmos.color = new Color(1f, 1f, .2f);
Vector3 gravity = .3f * this.gravityForce*this.gravityDirection;
Gizmos.DrawRay(this.Bob.transform.position, gravity);
Gizmos.DrawSphere(this.Bob.transform.position + gravity, .2f);
// Orange: Tension
Gizmos.color = new Color(1f, .5f, .2f); // Orange
Vector3 tension = .3f * this.tensionForce*this.tensionDirection;
Gizmos.DrawRay(this.Bob.transform.position, tension);
Gizmos.DrawSphere(this.Bob.transform.position + tension, .2f);
// Red: Resultant
Gizmos.color = new Color(1f, .3f, .3f); // red
Vector3 resultant = gravity + tension;
Gizmos.DrawRay(this.Bob.transform.position, resultant);
Gizmos.DrawSphere(this.Bob.transform.position + resultant, .2f);
/* * /
// Green: Pendulum side direction
Gizmos.color = new Color(.3f, 1f, .3f);
Gizmos.DrawRay(this.Bob.transform.position, 3f*this.pendulumSideDirection);
Gizmos.DrawSphere(this.Bob.transform.position + 3f*this.pendulumSideDirection, .2f);
/* */
/* * /
// Cyan: tangent direction
Gizmos.color = new Color(.2f, 1f, 1f); // cyan
Gizmos.DrawRay(this.Bob.transform.position, 3f*this.tangentDirection);
Gizmos.DrawSphere(this.Bob.transform.position + 3f*this.tangentDirection, .2f);
/* */
}
}
Weitere Glamour-Shots:










